Блог
I.What is an Instrument Cabinet?
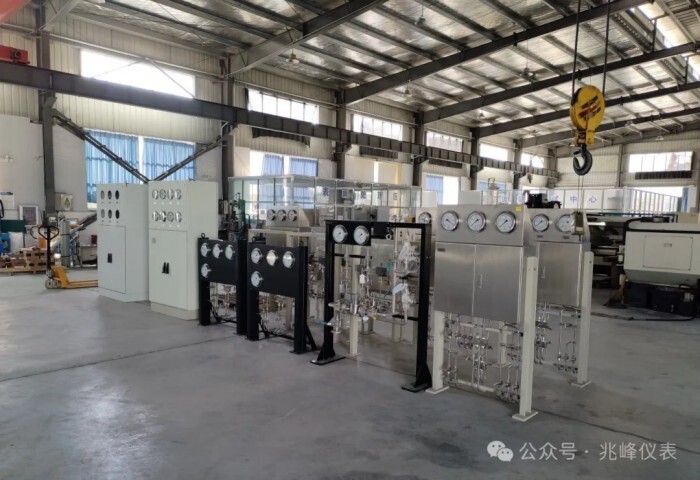

An instrument cabinet is an enclosed structure designed for installing and protecting electrical equipment, control systems, and various measuring instruments. It is widely used in refining, chemical, light industry, textile, defense, aerospace, metallurgy, power, pharmaceuticals, and machinery industries, serving as a key component to ensure the stable operation of automation systems.
II. Functions of Instrument Cabinets
1. Equipment Protection
Instrument cabinets provide dust-proof, moisture-proof, explosion-proof, and electromagnetic interference protection, ensuring the safe operation of internal electrical equipment and instruments in harsh industrial environments. Proper ventilation and heat dissipation prevent damage caused by high temperatures.
2.System Integration and Management
Instrument cabinets integrate various control devices, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), inverters, protective relays, as well as display and alarm devices. Centralizing these devices simplifies system design, wiring, and maintenance.
3.Signal Processing and Transmission
Instrument cabinets often contain equipment for receiving and processing signals from sensors such as pressure, temperature, level, and flow sensors. The signals are transmitted to the control center, ensuring real-time monitoring and accurate control.
4.Operation and Monitoring Platform
Some instrument cabinets are equipped with human-machine interfaces (HMIs) or monitoring devices, allowing operators to perform on-site monitoring and data input. These devices display real-time data and execute automated control tasks via preset programs.
III. Main Structure of Instrument Cabinets
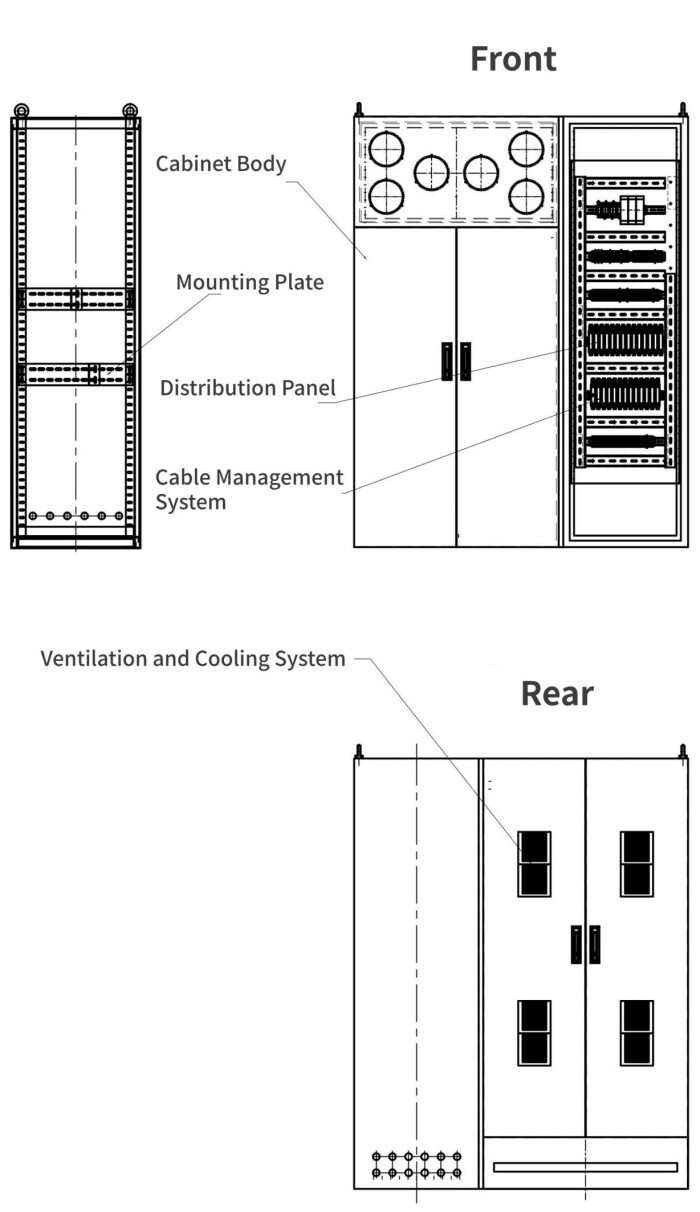
1. Cabinet body: Made of metal materials with high strength and good corrosion resistance, commonly cold-rolled steel plates or stainless steel.
2. Mounting plate: Internal panels for fixing instruments and equipment, providing flexible installation space.
3. Distribution panel: Used for power distribution and protection, ensuring safe power supply.
4. Cable management system: Organizes, secures, and protects cables, avoiding clutter and damage.
5. Ventilation and cooling devices: Natural ventilation or fan cooling reduces equipment operating temperature.
IV. Classification of Instrument Cabinets
1. Standard instrument cabinets: For general industrial environments, offering basic protection and management functions.
2. Explosion-proof instrument cabinets: Designed for flammable and explosive environments, ensuring safe operation under hazardous conditions.
3. Stainless steel instrument cabinets: Common in chemical and pharmaceutical industries, providing excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for humid or highly corrosive environments.
4. Intelligent instrument cabinets: Equipped with smart monitoring systems and remote operation modules for advanced automation and intelligent management.
V. Key Points for Cabinet Selection
1. Environmental requirements: Different environments require different protection levels, such as rainproofing for outdoor use or explosion-proof designs for hazardous areas.
2. Equipment quantity and layout: Cabinet size and internal space must accommodate the number and type of devices, ensuring neat installation and easy maintenance.
3. Heat dissipation and ventilation: For high-power devices, heat dissipation design must be prioritized to prevent overheating and failures.
4. Intelligent functionality: If remote monitoring or intelligent management is required, intelligent instrument cabinets are the best choice.
VI. Example from Zhaofeng Instruments
For example, the 1200MW nuclear power unit stator cooling water integrated instrument cabinet is designed for centralized installation of measuring instruments such as pressure transmitters, differential pressure transmitters, flow meters, and conductivity analyzers. It enables centralized monitoring and remote signal control of the stator cooling water system operating conditions.
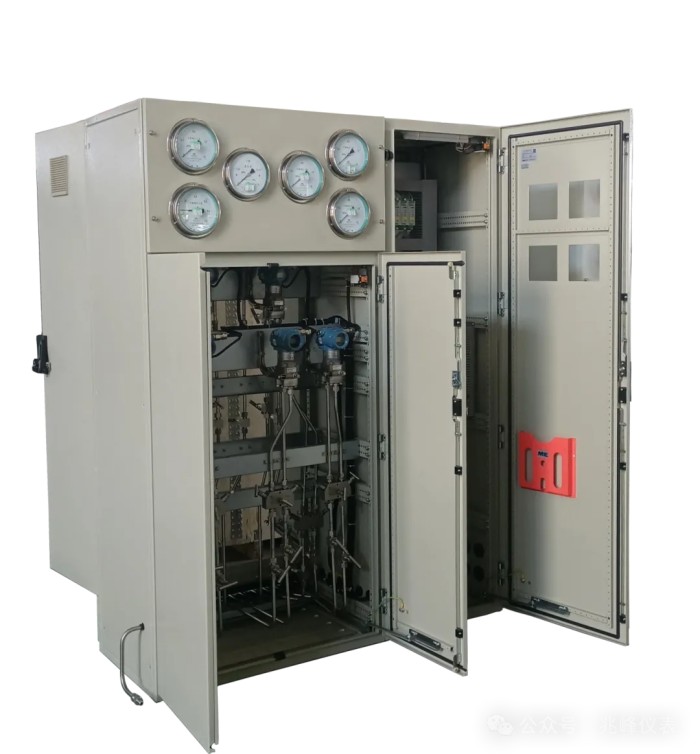

Considering requirements such as:
a. Seismic resistance (seismic fortification intensity VIII)
b. Relative humidity (0–100%)
c. Air quality (salt, dust, hydrogen-containing explosive mixtures)
d. Working medium (except deionized water)
e. Design temperature (85 °C)
f. Design pressure (1.6 MPa)
This cabinet features:
a. Dual-sided integrated structure (including electrical and instrument sections).
b. Explosion-proof components meeting GB/T3836 standards, including transmitters, power modules, isolators, conductivity meters, cables, and terminals.
c. High protection levels: IP52 for instrument section, IP54 for electrical section, with sealed connections and explosion-proof glands.
d. Corrosion resistance: electrostatic spray coating, with stainless steel (06Cr19Ni10) for fasteners, pipes, and accessories.
e. Strong structural integrity: cabinet made of carbon steel plates and profiles, thickness ≥ 2 mm.
f. Rational design and easy installation.
g. High sensitivity and reliability of instruments, supplied by qualified manufacturers and tested according to relevant standards, including calibration, performance tests, and pipeline pressure tests.
(Note: Custom designs are available according to customer requirements.)
VII. Future Development Trends

1. Intelligence: Integration of smart sensors, IoT technologies, and remote control modules for online monitoring and remote management, improving operational efficiency.
2. Modularity: Flexible designs supporting quick assembly and expansion to adapt to diverse production needs and scenarios.
3. Green and eco-friendly design: Use of energy-saving materials and devices to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact, aligning with sustainable development.
Instrument cabinets are an indispensable part of industrial automation systems. They not only provide protection for electrical equipment and control systems but also integrate control, monitoring, and signal processing functions. With ongoing technological development, future cabinets will become more intelligent and modular, playing an increasingly vital role in industrial applications.
